Page 63 - Electronic Navigation Cyber Book
P. 63
DIFFERENTIAL GPS (DGPS)
As has already been stated, the accuracy of GPS fixes can be vastly
improved using differential techniques. Experimental differential systems
have been in use for some years as part of earlier hyperbolic earth-based
navigation systems. DGPS is merely an improvement of those now
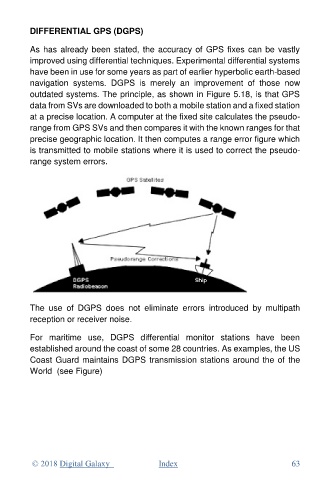
outdated systems. The principle, as shown in Figure 5.18, is that GPS
data from SVs are downloaded to both a mobile station and a fixed station
at a precise location. A computer at the fixed site calculates the pseudo-
range from GPS SVs and then compares it with the known ranges for that
precise geographic location. It then computes a range error figure which
is transmitted to mobile stations where it is used to correct the pseudo-
range system errors.
The use of DGPS does not eliminate errors introduced by multipath
reception or receiver noise.
For maritime use, DGPS differential monitor stations have been
established around the coast of some 28 countries. As examples, the US
Coast Guard maintains DGPS transmission stations around the of the
World (see Figure)
© 2018 Digital Galaxy Index 63